テストを書いてみよう
テストを書く前に、テスト対象になる処理が必要です。今回は、「与えられた City のリストから国ごとの人口の和」を計算する処理を書いてみます。
ヒント
- 国ごとにデータを分けて持つには
std::collections::HashMapを使えばいいでしょう - 国単位で集計するので map の key は
country_codeを使うといいでしょう country_codeが空文字列である City は、和を計算せず無視してください
参考実装
rs
use std::collections::HashMap;
//与えられた City のリストから国ごとの人口の和を計算する
pub fn sum_population_by_country(cities: Vec<City>) -> HashMap<String, i32> {
let mut map = HashMap::new();
for city in cities {
if city.country_code.is_empty() {
continue;
}
let entry = map.entry(city.country_code).or_insert(0);
*entry += city.population;
}
map
}このメソッドが期待した値を返すかどうか、テストを書いて確認していきましょう。
メソッド 1 つなど、小さい単位でのテストは、ユニットテストと呼ばれます。 ユニットテストは同じファイル内にテストを書くのが一般的です。
同じファイル内の一番下にテストを書いていきます。
rs
// #[cfg(test)] 属性を追加したモジュールはテストモジュールとして扱われる
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use super::{sum_population_by_country, City};
use std::collections::HashMap;
fn test_sum_population_by_country() {
// ここにテストを追加する
}
} まずは、空のリストを渡したときに、空のマップが返ってくることをテストしてみましょう。
rs
// #[cfg(test)] 属性を追加したモジュールはテストモジュールとして扱われる
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use super::{sum_population_by_country, City};
use std::collections::HashMap;
#[test]
fn test_sum_population_by_country() {
// ここにテストを追加する
let cities = vec![];
let result = sum_population_by_country(cities);
assert!(result.is_empty());
}
}書き終わったら、関数の左上またはモジュールの左上にある run test を押して、テストを実行してみましょう。

すると、VSCode の Output にテストの結果が表示されます。
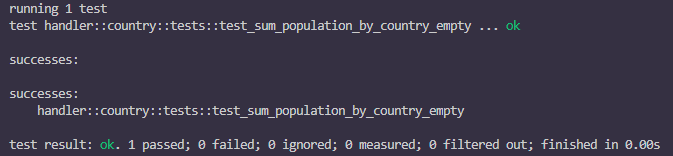
テストが正常に終了したことがわかります。
様々なケースをテストしてみよう
次に、 sum_population_by_country のテストをもう少し充実させてみましょう。
これから複数のテストを書くため、先ほどのテストの関数名を変更します。
rs
// #[cfg(test)] 属性を追加したモジュールはテストモジュールとして扱われる
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use super::{sum_population_by_country, City};
use std::collections::HashMap;
#[test]
fn test_sum_population_by_country_empty() {
// ここにテストを追加する
let cities = vec![];
let result = sum_population_by_country(cities);
assert!(result.is_empty());
}
}課題
次のテストを実装してください。
- 1 つの国のみのデータが入っている場合
- 複数の国のデータが入っている場合
- 空文字列の
country_codeが入っている場合
答え
1 つの国のみのデータが入っている場合
rs
#[test]
fn test_sum_population_by_country_single() {
let cities = vec![
City {
id: Some(1),
name: "Tokyo".to_string(),
country_code: "JPN".to_string(),
district: "Tokyo".to_string(),
population: 100,
},
City {
id: Some(2),
name: "Osaka".to_string(),
country_code: "JPN".to_string(),
district: "Osaka".to_string(),
population: 200,
},
];
let mut expected = HashMap::new();
expected.insert("JPN".to_string(), 300);
let result = sum_population_by_country(cities);
assert_eq!(result, expected);
}複数の国のデータが入っている場合
rs
#[test]
fn test_sum_population_by_country_multiple() {
let cities = vec![
City {
id: Some(1),
name: "Tokyo".to_string(),
country_code: "JPN".to_string(),
district: "Tokyo".to_string(),
population: 100,
},
City {
id: Some(2),
name: "Osaka".to_string(),
country_code: "JPN".to_string(),
district: "Osaka".to_string(),
population: 200,
},
City {
id: Some(3),
name: "New York".to_string(),
country_code: "USA".to_string(),
district: "New York".to_string(),
population: 300,
},
City {
id: Some(4),
name: "Los Angeles".to_string(),
country_code: "USA".to_string(),
district: "California".to_string(),
population: 400,
},
];
let mut expected = HashMap::new();
expected.insert("JPN".to_string(), 300);
expected.insert("USA".to_string(), 700);
let result = sum_population_by_country(cities);
assert_eq!(result, expected);
}空文字列の country_code が入っている場合
rs
#[test]
fn test_sum_population_by_country_empty_country_code() {
let cities = vec![
City {
id: Some(1),
name: "Tokyo".to_string(),
country_code: "JPN".to_string(),
district: "Tokyo".to_string(),
population: 100,
},
City {
id: Some(2),
name: "Osaka".to_string(),
country_code: "".to_string(),
district: "Osaka".to_string(),
population: 200,
},
];
let mut expected = HashMap::new();
expected.insert("JPN".to_string(), 100);
let result = sum_population_by_country(cities);
assert_eq!(result, expected);
}実装が終わったら、モジュールの左上にある run test を押して、テストを実行してみましょう。
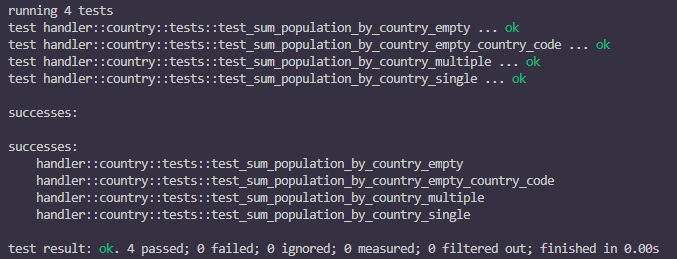
モジュール内の全てのテストが成功したことを確認できます。